President Lyndon Johnson declared a war on poverty and America, unlike Vietnam, won that war. World War One and Iraq remind us that some wars, even though we triumphed, have to be fought again. Such is the case with LBJ’s war on poverty. We won it, but now there’s a new war and we’re losing it thanks to the enemy within, a fifth column of Republican extremists who don’t want to pay their fair share.
For more on this we talked with Greg Kaufmann one of America’s leading voices for the poor.
Greg Kaufmann is the former poverty correspondent to The Nation and a current contributor. He serves as an advisor to the Ehrenreich Hardship Reporting Project and the Half in Ten Campaign. Through his writing he seeks to increase media coverage of poverty, share new research, elevate the voices of people living in poverty and offer readers opportunities to get involved with organizations working to eradicate poverty. Melissa Harris-Perry calls Greg “one of the most consistent voices on poverty in America.” Greg has spoken at numerous conferences and been a guest on Moyers & Company, MSNBC’s Melissa Harris-Perry, Tavis Smiley on PBS, NPR’s Radio Times with Marty Moss-Coane, Here & Now, Your Call, The Thom Hartmann Program, Stand Up! with Pete Dominick and The Matthew Filipowicz Show, as well as various local radio programs. His work has also been featured on CBSNews.com, NPR.org, WashingtonPost.com, and BusinessInsider.com. He serves as an adviser for Barbara Ehrenreich’s Economic Hardship Reporting Project. He graduated from Dickinson College and studied creative writing at Miami University (Ohio). He lives in his hometown of Washington, DC, with his wife, son and two daughters.

Greg is a frequent guest on Bill Moyers’ show. As a press spokesman for L.B.J. Moyers was on the front lines in the war on poverty.
We spoke with Greg about poverty in America.
David: You know, you’re a terrific writer, and before we start, I want everybody who’s listening to read your piece on “The Nation’s Website.” It’s up right now. It’s entitled “Confronting Congressional Hunger Games,” and I want to congratulate you on this piece. I’ll post the link to it on our website. Everyone has to read this article. It’s called “Confronting Congressional Hunger Games.” It’s up on The Nation’s website right now. It’s loaded with hyperlinks, just so you know that Greg Kaufmann doesn’t make things up.
Folks, you can decide not to pay attention to hunger in America, but read this article, because nobody can say you didn’t know. You can think whatever you want about people on food stamps, but you need to read this article so at least nobody can ever say you didn’t know. It is a great article, and if you’re on the right side, our side, this article will provide you with pretty much all the ammunition you’re going to need to change minds. People need to know. And so, again, Greg, I thank you for this article. I can’t wait to talk to conservatives because of this article. It’ll be like shooting fish in a barrel. Unfortunately, we can’t eat those fish, and people are starving.
Greg Kauffman: Yeah, David, well, thank you very much.
David: We’re out of time. Thanks for being on the show. Bye-bye.
Greg: I understand, your lordship. No, I thank you for that nice intro, and, yeah, I get sad and angry, too. I think it’s a particularly frustrating time. I mean, covering the poverty beat’s not great for morale anyway most of the time. Yeah, the SNAP food stamp votes and the farm bill votes of late have definitely made for some trying times, mostly for the people who need that assistance, of course.
David: Yeah. Before we dig into this and roll up our sleeves and talk about the farm bill . . .

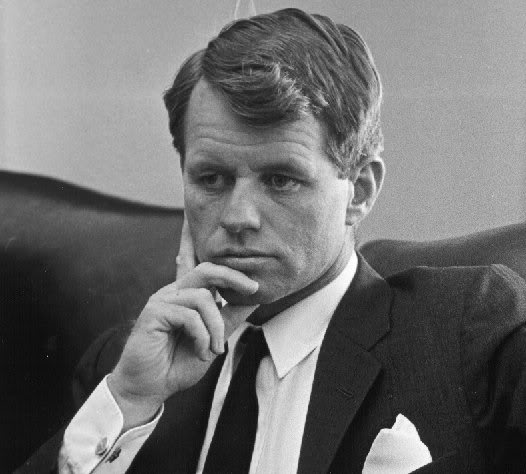
Born into great wealth Senator Robert Kennedy spent the last years of his life learning about and speaking up for America’s poor.
Greg: Yeah.
David: . . . if I were a Muslim and somebody told me the United States is a Christian nation, I’d say, “Good, let your religion take the brunt of this. Let your religion take responsibility for this,” because this is embarrassing.
Greg: Right.
David: This is really embarrassing, so if people want to call this a Christian nation, knock yourself out, have at it, because I would be ashamed to associate any religion with our country.
Greg: It’s obscene! Before we had the food stamp program, back in the late ’60s, or mid ’60s, there were childrenwith bloated bellies in Mississippi and Appalachia. You know, Bobby Kennedy, Peter Edelman went down there, Marion Wright, who’s now Marion Wright-Edelman, showed them around towns where they met these kids with the kind of hunger and malnutrition that we associate with third world countries now, and we say, “Well, we don’t have that in the States.” And, yeah, we don’t have that, and that’s because we created a federal food stamp program. Yeah.
David: I’m told the federal government can’t do anything right, that if it’s left to the federal government, everybody’s just going to fail.
Greg: Yeah.
David: What was the poverty rate in America before Lyndon Johnson declared a war on poverty, and what was the poverty rate after his war on poverty?
Greg: The impact of public policy from 1964 to 1973, the poverty rate fell by 43 percent. I’m not a numbers guy, actually, but I keep a list of numbers, because I’m not a numbers guy.
David: Right. And by the way, it’s in your article. That’s why I asked you.

By all accounts President Johnson’s war on poverty was a success. Unfortunately Republican attempts to undermine that victory has also been a success.
Greg: Yeah. And at the end of my article, I keep something called vital statistics that’s part of the end of my blog every Friday, and part of the reason I do that is for myself to keep those numbers present, but more it’s because people have no idea. I mean, I didn’t before I started working this beat and the statistics about poverty. So when they say the war on poverty failed, they should look at how the poverty rate fell during the war on poverty.
And further, even more recently, if you look at 2010, Arloc Sherman, who’s a great policy analyst at the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, looked at the impact that the safety net programs had on poverty in 2010. We had a 15 percent rate of poverty that year. Your listeners should know that the poverty rate and the poverty level is just $18,000 for a family of three, so we’re talking about people who lived on less than $18,000, and it was 15 percent that year. I think that’s like 45 million Americans, 46 million Americans, and it would’ve been almost double, 28 percent, without the safety net.
So Congressman Ryan says quite frequently, “We’re not looking at the results of our programs. We’re just looking at how much money we spend.” Baloney. He’s looking just at how much money we spend. He’s not looking at the results. He’s complaining about the money we spend. He’s not looking at the fact that poverty would be twice as high without the programs we have in place, and when you talk about getting angry, I mean, those are the kinds of moments where, yeah, anybody who believes in sort of rational analysis, not to mention the kind of values you were talking about, Christian, Jewish, Muslim, humane values, that should make you pretty angry.